What is the Role of the Moon’s gravitational force on ocean tides?
Have you ever wondered what causes the frequent tides in the oceans? Well, the moon’s gravitational force has something to do with it. To learn more, here is a short explanation of what happens during tidal events.
The gravitational attractive force results in tidal forces. Therefore, the moon’s gravitational force is responsible for the rise and fall of Ocean Tides. The tidal force is caused by the moon’s gravitational pull. The tidal force causes Earth and its water to bulge out on the sides closest to and farthest from the moon. These water bulges form due to high tides.
The moon’s gravity pulls on different parts of our planet as it rotates. Even though the moon has only about 1/100th the mass of Earth, it has enough gravity to move things around because it is so close to us. The moon’s gravity pulls on the land as well, but not enough for anyone to notice (unless they use special, really precise instruments). However, when the moon’s gravity pulls on the water in the oceans, someone is bound to notice. Water moves much more easily, and it wants to bulge in the direction of the moon.
What is the difference between the high and the low tides?
The moon’s gravity creates a tidal force which in turn attracts earth oceans, thereby creating a side bulge (high tide) towards the direction of the moon directly facing the Earth. Subsequently, another bulge (high tide) forms in the earth oceans on the other side or direction facing away from the moon. The low tides are associated with sides at 90° with the moon (N and S in the figure below). This simply explains why there are usually two high tides happening on Earth at the same time every day. Learn more about the low and high tides we see in the oceans.
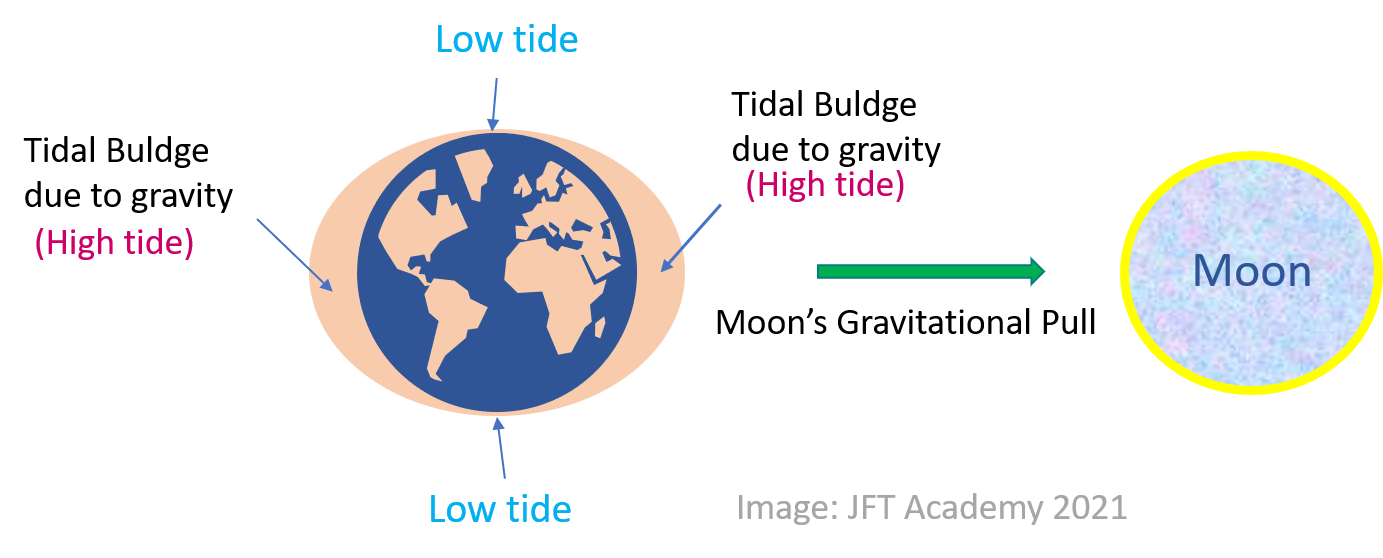
Whereas the Earth and the Moon are both rotating and or revolving around the sun, the Earth’s gravity keeps the moon in orbit around it. This arrangement in the solar system causes the gravitational force of both the sun and the moon to affect the earth oceans. The moon’s gravitational force is responsible for the primary tide, which is normally higher as compared to the second tide on its far side. Nevertheless, the Earth’s centripetal force and partly the sun’s gravity effect on Earth trigger the oceans on the far side (away from the moon’s direction) of the Earth to move out or rather bulge (as a counter-balance) commonly referred to as the secondary tide. In the figure above, the Earth’s side facing the moon firms the primary high tide. The left side of the diagram demonstrates the secondary high tide acting as a counter-balance.
Benefits of the Moon’s gravitational force?
Tides have an impact on various areas of ocean life, such as fish and ocean plant reproduction. Tidal currents carry floating plants and animals between breeding areas and deeper waters. The tides help in the removal of pollutants and for the circulation of nutrients required by ocean plants and animals. To some forms of life on Earth, the advance and retreat of tides create useful habitats. The gravitational effect of the moon keeps the degree of the Earth’s rotation on its axis constant. This tilt is what maintains the repeatable cycle of climate as the Earth orbits the sun. Consequently, the moon also stabilizes Earths Climate. The existence of the moon, therefore, is responsible for the survival of terrestrial life on Earth.
Get more information and illustrations about the moon and the ocean tides SciJinks website.
Contacts us for more information and illustrations for this or any related topic.
Article By:
Bonface Wanguba